A winning business plan is core to your business’s success, whether you want to start or expand an existing one. This will also help you map your strategies commendably and act as an instrument of attraction for investors and securing finances. In this article, we take you through the 10 steps toward a winning business plan, using real-life examples to walk you through.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a formal document that details the objectives of any undertaking and how those objectives will be realized. It is used as a guide for initiating or growing the business. It, therefore, captures the vision and mission relating to the goals and operation procedures for investors and potential partners.
A business plan is important to a person just getting into business or expanding his existing one, as it charts the way to success. It may even detail the vision and strategies of the business to important stakeholders.
| Step No. | Steps to create a winning business plan |
| 1. | Executive Summary |
| 2. | Company Description |
| 3. | Market Research and Analysis |
| 4. | Organization and Management |
| 5. | Product Line and Service Offering |
| 6. | Marketing and Sales Strategy |
| 7. | Funding Request |
| 8. | Financial Projections |
| 9. | Appendix |
| 10. | Review and Revise |
| Conclusion |
Top 10 Steps to Create a Winning Business Plan
Step 1: Executive Summary
- What it is:
The executive summary will be the first part of your business plan but is written last. It summarizes your whole plan and emphasizes all the main points. Consider it the elevator pitch for your business.
- Why it matters:
Investors often make initial decisions based on the executive summary. If that doesn’t grab them, they might not make it to the rest of the plan.
- Example:
When Elon Musk pitched Tesla Motors, his executive summary was not about making electric cars but rather the vision of a sustainable future wherein Tesla would lead from the front to drive the automobile industry into a new world order of clean energy. That big-picture thinking captured the investors and was key in raising initial funding.
- How to do it:
- Start with your business’s mission statement.
- Describe briefly a product or service, your target market, and your financial highlights. Concise, yet compelling and to the point.

Source: Studocu
Step 2: Company Description
- What is it?
A company description entails detailed information concerning your business, such as its history, structure, objectives, and the problems it solves.
- Why does it matter?
Well, it puts your readers into perspective as far as your business is concerned. And it shows you are a credible firm.
- Example:
When Starbucks was a small coffee shop in Seattle, the company described its commitment to providing quality beans worldwide. This focus on quality set it apart from other shops and was the basis on which they started building their brand.

Source: SlidePlayer
- How to do it:
- Describe the history of your business and how it’s evolved.
- Describe the legal structure of your business, including LLC or corporation.
- List your business goals and describe what distinguishes your business from others.
Step 3: Market Research and Analysis
- What is it?
Market research and analysis cover the research of your industry, target market, and competitors. In this section, you should reveal your knowledge about what happens in your industry.
- Why it’s important:
Any investor wants to be convinced that you have done your homework as for the market you are going to enter, meaning you have initially identified opportunities and possible challenges associated with entering that particular area.
- Example:
The founders of Airbnb conducted some market research before the venture took off. They found that people were not inhibited about renting their homes to tourists; they just needed a website to offer such services. Their research confirmed a gap in the market, which they filled.
How to do it:
- Profile the target market and customer demographics.
- Research the potential growth, trends, and size of the market in the industry.
- Conclude who your competitors are and the strengths and weaknesses of the firms.
Step 4: Organization and Management
- What it is:
This section covers the organizational structure of your business and introduces your management team. Here, you must highlight your team’s years of work and experience.
- Why it matters:
Investors want to know who is behind the wheel. A good management team might be a prime determinant in attracting an investment.
- Example:
When Google was founded, Larry Page and Sergey Brin were two of its founding members. However, they knew that it was an equally important task to be able to put seasoned management into place. So they brought in Eric Schmidt as chief executive. It turned out that his experience as a former executive of technology companies was essential for the early years of Google.

- Steps to how to do it:
- Prepare an organizational chart explaining the team members and their experience.
- Clearly explain the responsibility that each one holds.
Step 5: Product Line or Service Offering
- Description:
Here, you describe in detail the products or services your business offers. This includes what you will be offering, how it benefits your customers, and your development plans.
- Why it’s important:
What are you selling, and why will your customers want to buy it? This is where you need to emphasize the value the product or service will add to buyers.
- Example:
When Apple launched the iPod, it didn’t say, “Here’s a portable digital music player.” It was a device that could put “1,000 songs in your pocket,” touting the convenience and redefining how people listened to music. That articulation of value proposition lets it own the market.
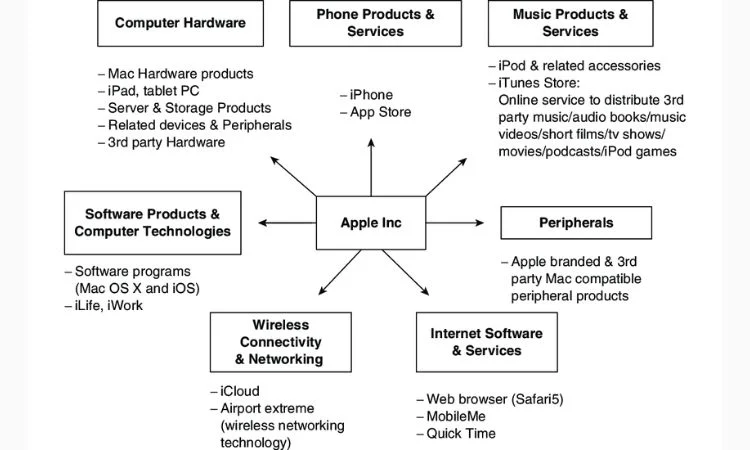
Source: Research Gate
- How to do it:
Describe your product or service.
Describe how it serves the need for your target market.
Discuss whether there is some possibility for further development or innovation.
Step 6: Marketing and Sales Strategy
- What it is:
Your marketing and sales strategy depicts how to obtain and also service customers. This section should discuss the marketing channels, the sale process, and strategies for acquiring customers.
- Why it matters:
Even the best product does not sell itself. You must implement a well-articulated way of reaching your target audience and converting leads to customers.
- Example:
Dollar Shave Club disrupted the razor market with a simple but effective way of reaching their prospects. Their viral video campaign garnered millions of views, and the subscription-based sales model made it easy for customers to get razors delivered to their doorsteps. It was an innovative approach to grow their market share within a short time.
- How to do it:
- Identify your target market and buyer personas.
- Choose your marketing channels: social media, email, and content marketing.
- Skim the outline of your sales process from lead generation to close of sale.
Step 7: Funding Request
- What is it?
If you are seeking funding, this is the section in which you summarize your funding requirements, including the amount, what it will be used for, and your proposed terms.
- Why it is important:
You need to let investors know how much money youn are asking for and what it is for. This is often where clarity and reasonability of funding requests make all the difference between success and a pass.
- Example:
For instance, when raising capital for Amazon, Jeff Bezos estimated precisely the amount of capital needed to scale the business and precisely what he would do with the money. In his estimation, the funds were needed to create inventory, invest in technology, and market the company for rapid growth. This transparency eventually won him the financing he required.
- How to do it:
- Prescribe the amount required in funding.
- Describe the intended use of funds, such as product development, marketing, and operations.
- Include terms, if any, with respect to proposed equity/debt.
Step 8: Financial Projections
This section should be prepared with your financial projections or the basic financial statements: an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. A break-even analysis must also be included in this section, along with a projection for at least three to five years.
- Why it matters:
This will greatly help you convince investors that your business is viable financially and that you also have a credible plan for its profitability. Financial projections serve as useful in setting milestones and monitoring progress.
- Example:
At the time when Facebook was still a college social network, its financial projections were on the conservative side due to continuous user growth and incremental revenue streams such as advertising. The realistic projections lured early investors, who saw potential long-term profitability.
- How to do it:
- Attach comprehensive income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
- Attach your break-even analysis, showing when you expect to break even.
- Include assumptions supporting your projections.
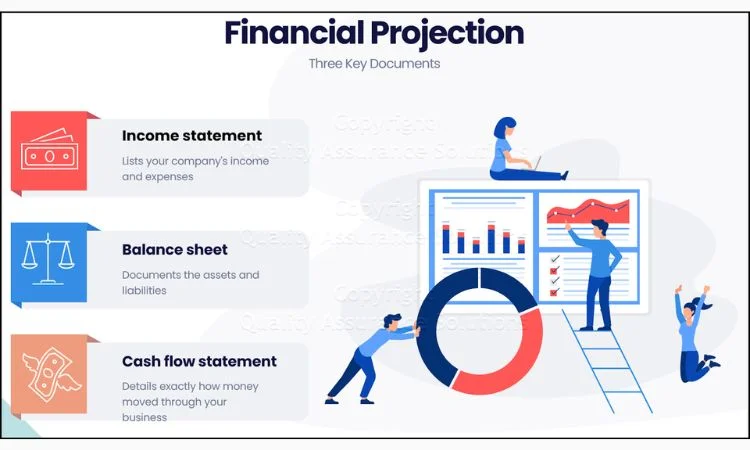
Source: Quality Assurance Solutions
Step 9: Appendix
- What is it?
The appendix is additional information that supports your business plan. This could be resumes, legal documents, product pictures, or research data.
- Why it matters:
The appendix is a reference that provides more detailed information for readers. Not everyone will read it, but its presence shows completeness.
- Example:
The founders of Warby Parker had an appendix of detailed market research, pictures of prototypes, and testimonials from customers when pitching their startup to investors. More information helped investors feel better about the potential of the business.
- How to do it:
Attach any supporting documents to your plan, such as patents, product pictures, or contracts.
The appendix must be well-organized and easy to navigate.
Include in the appendix only information that complements your business plan.
Step 10: Review and Revise
What it is:
The final step is to review and revise your business plan. This covers proofreading and refining content for mistakes or upon reception of feedback.
- Why it matters:
A polished business plan reflects your professionalism and attention to detail. It also shows that one takes the plan seriously, and the vision comes out clear.
- Example:
Before launching Spanx, Sara Blakely spent months honing her business plan. She asked for input from mentors and investors, refining her plan until her value proposition was more articulate and her financial projections were stronger. That close scrutiny of her plan helped her to develop a plan that would prove successful.
- How to do it:
- Spell and grammar-check your business plan;
- Have your plan reviewed and critiqued by mentors, colleagues, or advisors.
- Revise for clarity and to strengthen arguments.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, writing a successful business plan is the most potent way to ensure the success and growth of your business. Follow these 10 steps in this step-by-step guide on how to write an engaging executive summary, conduct thorough market research, complete your financial projections, and perfect your plan to lay a strong foundation for the future of your business.
A business plan is a living and breathing document. As your business grows and evolves, so too will your plan. Ongoing review and revision against it allow you to stay on track and adapt to those key changes in circumstance. With one concise, well-detailed, well-researched business plan, you are not just planning your future but creating it.













