Google’s recent AI advancements have once again stirred the tech world, particularly with its generative AI capabilities in Google Search. At the heart of this buzz is an amusing yet concerning incident where Google’s AI claimed that cats had been found on the moon. This bizarre assertion is part of a larger issue with AI-generated content sometimes producing misleading or outright false information.
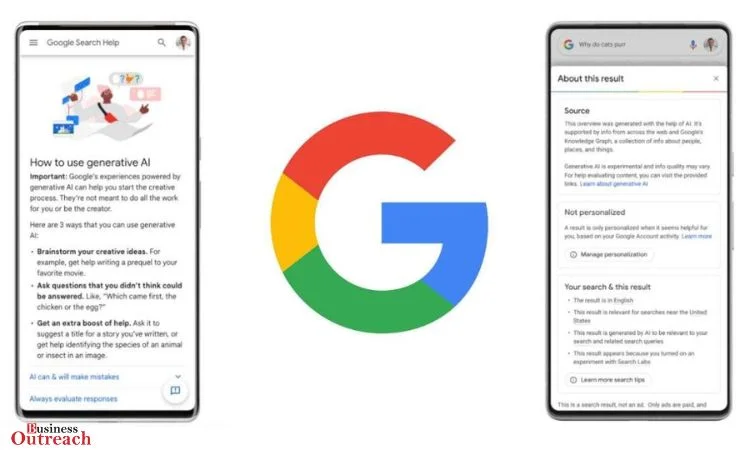
During the Google I/O 2024 conference, the company introduced significant updates to its search engine, emphasizing AI-generated “Overviews.” These overviews are designed to provide quick, comprehensive answers to user queries, leveraging the latest version of Google’s AI, Gemini【9†source】【10†source】. Despite their potential to enhance user experience by simplifying complex searches, these AI tools have also demonstrated the propensity to generate inaccurate responses, as evidenced by the whimsical claim about lunar felines.
The integration of AI Overviews is a milestone in Google’s ongoing evolution, promising to transform how users interact with search results. This technology aims to reduce the time users spend sifting through multiple sources by summarizing information from across the web. The AI is particularly useful for complex queries and planning tasks, which traditionally required more extensive research.
However, the rollout of these AI capabilities has not been without controversy. The erroneous claims about moon cats highlight a broader issue of reliability in AI-generated content. AI models, despite their sophistication, can sometimes misinterpret or fabricate information based on the data they were trained on. This incident underscores the critical need for improved accuracy and verification processes in AI systems to prevent the spread of misinformation.
Beyond the quirky errors, the new AI-powered search features are set to significantly impact web traffic and the digital advertising landscape. AI Overviews are expected to reduce the visibility of traditional search results and ads, potentially diminishing traffic to external websites. This shift could have financial implications for content creators and publishers who rely heavily on search engine traffic for revenue.
To mitigate these impacts, Google has assured that it will focus on driving valuable traffic to publishers through its AI Overviews. The company notes that during testing, AI Overviews led to an increase in the number of searches and user engagement, suggesting that users often start with AI-generated summaries but continue to explore deeper through traditional links.
Despite these assurances, there are concerns within the digital ecosystem. Some experts fear that AI Overviews could siphon traffic and ad revenue away from smaller websites, consolidating it within Google’s ecosystem. This scenario might lead to a significant redistribution of wealth from independent content creators to large tech companies, echoing concerns about the dominance of Big Tech in various sectors.
Google’s push towards integrating more AI into its services is part of a broader strategy to stay ahead in the competitive landscape of AI-driven search engines. The company is not alone in this endeavor, facing competition from AI systems like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, which also integrates generative AI to enhance search and user interaction experiences. This competitive pressure drives rapid innovation but also necessitates careful management of the ethical and practical implications of AI technology.
In conclusion, while Google’s AI advancements in search promise significant benefits in terms of efficiency and user experience, they also bring to light challenges related to accuracy, reliability, and the broader impacts on the digital economy. As AI technology continues to evolve, ongoing efforts to refine these systems and address their shortcomings will be crucial in harnessing their full potential while mitigating negative repercussions.















