Investing your cash into several assets might appear smooth for developing wealth, but becoming a successful investor proves to be more challenging than imagined.
Most retail traders—the ones without expert funding training—lose money each year. Among the many reasons for this, one of the most common challenges is a lack of time to thoroughly research stocks and investments and uncertainty about what key information to focus on.
In other words, without in-depth studies, you are much more likely to incur losses. But here’s the good news: through specialization in a few key investment strategies and charts, you could minimize both your losses and the amount of time you have to devote to your studies. Read on to learn the five critical stock charts every investor must know for more effective investing.

Image credit: Share India
Understanding chart patterns in the stock market
Learning chart patterns is one of the most important aspects of technical analysis, but it’s certainly not that easy to learn. In practice, however, once mastered, it can prove an excellent tool in helping predict a market’s future movement. Here are 10 of the must-know chart patterns for any trader.
Thus, in its simplest form, a chart pattern can be defined as a visual design formed on a price chart. It serves as a guide toward predicting the future behaviour of prices concerning historical movements. These are the foundation of technical analysis’s architecture and can be recognized by traders as far as their knowledge of how what they see is interpreted.
Don’t Miss: Master the Stock Market in 30 Days: A Beginner’s Guide
The best chart pattern is one that doesn’t exist as such; this is because no two chart patterns deal with the same thing or even for the same type of trend in different markets. Many traders tend to apply candle charts when tracking the movement of market opening and closing to monitor chart patterns.
That said, it becomes evident that the proper understanding of which chart pattern suits the particular market in which one trades is critical. Using a wrong pattern, or the absence of choosing an appropriate one, often leads to lost opportunities and possible losses.
Before dealing with how to analyse chart patterns, it is essential to understand the meaning of support and resistance levels in finance. Support is the point at which an asset has further to fall in value before it begins to rise again, while resistance is the price that an asset cannot seem to rise above before it falls back down again.
The resistance and support levels are reached by the continuous battle between buyers and sellers, between supply and demand. When the buyers overwhelm the sellers, prices normally rise; when demand from the supply side is much greater than from the demand side, prices fall.
Types of Stock Chart Patterns
Different chart patterns are meant for different conditions in the market. Some are better suited for the volatile kind, while others work well under stable market conditions. Most patterns can be best used when a bullish (rising) trend is taking place, while others are said to be best in a bearish (declining) market trend.
Stock chart patterns are generally divided into three categories, which are listed below:
1. Continuation Patterns
Suggest that the current tend is likely to persist. They indicate that the existing price movement will continue in the same direction once the pattern is completed.
2. Reversal Patterns
signals that a trend could be about to change direction. These patterns can help traders anticipate when a bullish trend may turn bearish or vice versa.
3. Bilateral Patterns
suggest high market volatility, with price movement potentially going in either direction. Traders should be prepared for the possibility of significant price fluctuations, as the market can move unpredictably.
Top 5 Important Stock Chart Patterns Every Investor Must Know
| Sr. No. | Important Stock Charts Patterns |
| 1 | Heads and Shoulders |
| 2 | Double Top |
| 3 | Double Bottom |
| 4 | Cup and Handle |
| 5 | Wedges: Bullish and Bearish Reversal Indicators |
1. Heads and Shoulders – Stock Chart Patterns
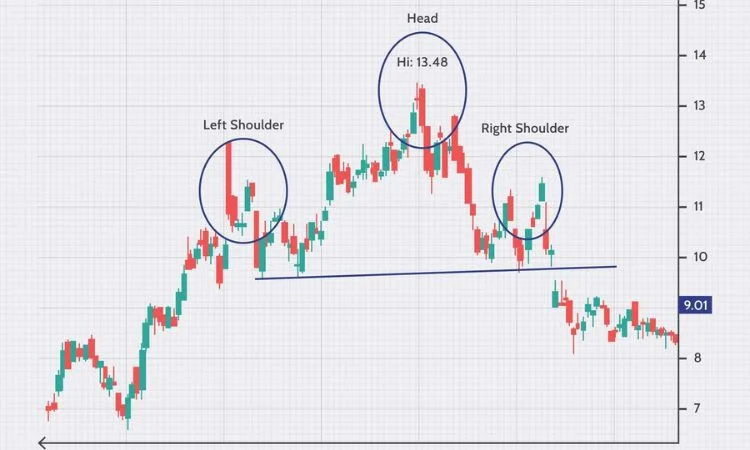
Source: Investopedia
The head and shoulders pattern is one of the most widely recognized patterns in technical analysis, a pattern that usually presents bullish-to-bearish reversal trends. The head and shoulder pattern consists of three formations—the larger peak in the middle is called the “head,” whereas smaller peaks called “shoulders” appear flanking it. Generally, this pattern appears at the end of an uptrend, indicating that the momentum gains of the market are stalling and thus setting the stage for a market reversal.
Structure of the Head and Shoulders Pattern
Left Shoulder: The first peak forms after the upward movement followed by a pullback to the neckline, which is the support line connecting the low points of the first peak and the trough.
Head: The peak, which is higher than the previous, shall attain the apogee of the pattern followed by a retracement towards the neckline.
Right Shoulder: The third peak will be smaller than the head and will also replicate the symmetry of the first shoulder, after which the prices move back to the neckline.
Neckline: This is the major support level because when the price breaks below the neckline after the third peak, it confirms the pattern for a potential bearish downtrend.
How to Trade the Head and Shoulders Pattern
Traders often establish a short position whenever the price breaks below the neckline to highlight a bearish movement. The target price would usually be measured from the head until the neckline while positioning the stop loss just above the right shoulder.
Despite such a strong pattern, this also needs to be validated and confirmed using other technical instruments to avoid false breakouts.
2. Double Top – Stock Chart Patterns
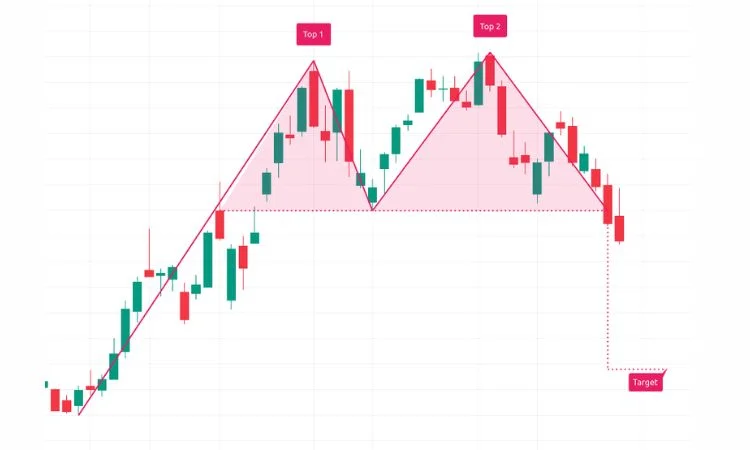
Source: ICICI Direct
The double top is a chart pattern that is applied very often by most traders as an indication of a bearish trend reversal; it typically arises after a long uptrend suggesting that the price is just about to change direction.
Double Top Pattern Structure
First Peak: Then the asset price turns to make the first peak. A subsequent price pullback to a support level occurs, which often retraces part of the previous move.
Second Peak: Price again rises to form the second peak that can be even closer to, if not greater than, the first one. A failed second peak typically fails to surpass the first one and indicates a loss in buying momentum.
Neckline: It is the support level formed after the first pullback. In the case of the second peak, if the price breaks below that neckline, then it confirms the double top pattern, and this might indicate a reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
How to Trade the Double Top Pattern
In most cases, a trader will opt for a short trade when the price penetrates the neckline suggesting the onset of the bearish reversal. Traders can compute a price target by using the distance between the two peaks and taking that away from where the neckline has been broken. A stop loss can be strategically placed above the second peak to safeguard against false breakouts.
Must Read: 7 Warren Buffett Tips for Smart Stock Investing
3. Double Bottom- Stock Chart Patterns
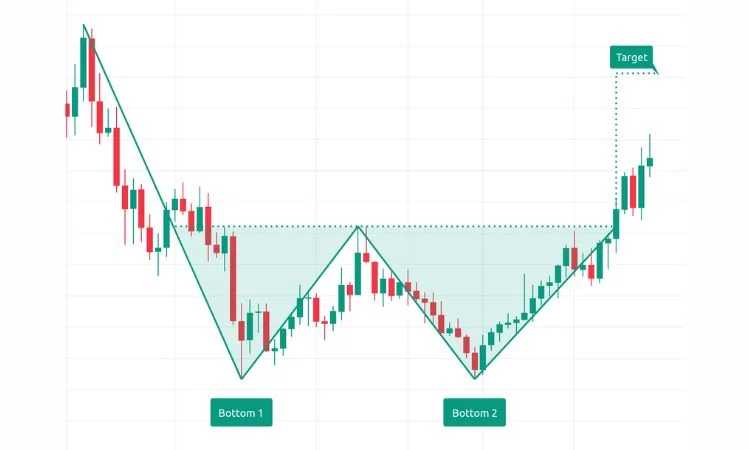
Source: ICICI Direct
The double bottom pattern plays a crucial role in chart analysis for traders to spot a possible upward shift in market trends. This pattern takes shape after a long period of falling prices, hinting that the market might soon change course and start to climb.
Double Bottom Pattern Structure
First Drop: The pattern kicks off when the asset’s value takes a big hit, falling below an important support level. A short recovery follows, with the price climbing to a resistance point.
Second Drop: The price then falls again, testing the same support level as before, but it doesn’t go any lower. This creates the second bottom of the pattern, often showing sellers losing steam.
Breakout: After the second bottom forms, the price begins to rise once more, pushing past the resistance level. This breakthrough marks the end of the downward trend and the start of a potential upswing.
How to Trade the Double Bottom Pattern
Traders often buy stocks when the price goes above the resistance level after the second bottom forms. This signals a bullish trend reversal. To set the target price, they measure the gap between the bottoms and add it to the breakout point. To protect themselves from sudden market shifts, they put a stop loss just under the second bottom.
4. Cup and Handle – Stock Chart Patterns
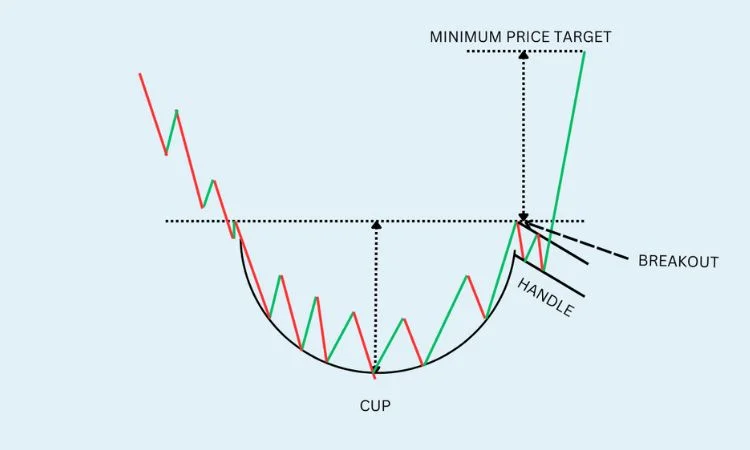
Source: Equentis
Traders often use the cup and handle pattern to spot chances where a downward trend changes into a new upward trend. This well-known bullish continuation pattern shows up after a time of negative market feelings. It hints that the overall trend is going to pick up again in a positive direction.
The Cup: The pattern starts with a curved bottom looking like a cup’s shape. This stage shows a drop in price and then a slow recovery, creating a U-shape. The cup has a steady fall followed by a smooth rise showing that selling has slowed down and buyers are taking charge.
The Handle: After the cup forms, the price often pulls back for a bit in a smaller range, making the “handle.” This pullback is a small dip between two parallel lines, much like a wedge. The handle shows a time when prices settle or fall before they go up again.
Breakout and Continuation: When the price goes above the resistance level at the top of the cup, this breakout points to the bullish trend going on. This would confirm that the market sentiment is once again bullish and this asset can be expected to continue its advance.
How to Trade the Cup and Handle Pattern
Traders are likely to enter a long position when the price breaks above the resistance line formed on top of the cup. The cup’s depth is sometimes used to calculate the price target, which is projected from the breakout point. A stop loss is usually placed just below the handle to manage risk.
5. Wedges: Bullish and Bearish Reversal Indicators
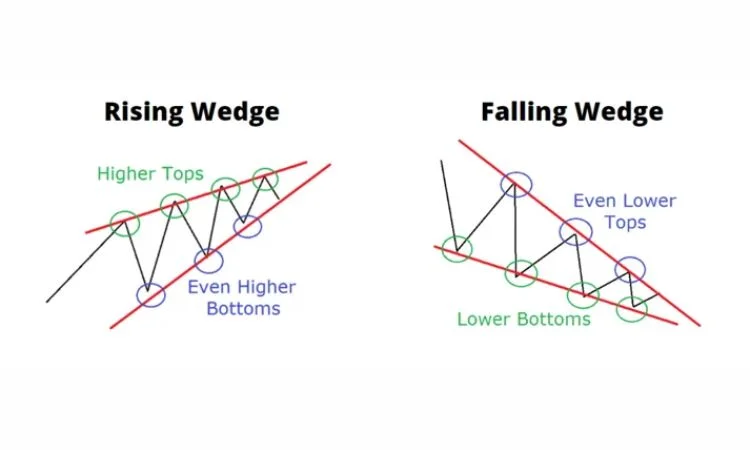
Source: Tradingsim
Wedges are chart patterns representing the tightening of an asset’s price movements between two sloping trendlines. Two types of wedges are there, a rising wedge and a falling wedge, and they are essentially consolidations leading up to a breakout.
Rising Wedge Pattern
There is the rising wedge pattern composed of two trendlines slanting upwards. The support line in this pattern slopes steeply, and a resistance line slopes slightly lower than it. That means the increasing price grows weak upwards. In case a rising wedge pattern emerges, it indicates that the buyer lost control gradually while the sellers acquired control. Thus, in case the price breaks below support, there tends to be a bearish reversal and a more chronic decline in the price direction.
Falling Wedge Pattern
This is a falling wedge with the resistance line sloping down more steeply than the support line. On a falling wedge, the deceleration of the price decline slope happens, and the market can prepare itself for a turnaround; when the price crosses over the resistance line, there’s an indication that suggests there will be a bullish reversal to follow, meaning that the price of the asset could go up.
How to Trade Wedge Patterns
In a rising wedge, the trader will tend to look to go short when the price breaks through the support level and anticipates a bearish drop.
Conclusion
Head and Shoulders, Double Top, Double Bottom, Cup and Handle, and Wedges—the charts are indispensable tools with which traders explain and foresee the future. Such an interpretation of charts makes clear points of support and resistance for entry or exit as well as provides early clues for a potential reversal.















